Understanding the Role of an Attorney General
Have you ever wondered about the role of an Attorney General (AG) in the legal system? The Attorney General is a crucial figure in many countries, serving as the chief legal advisor to the government and leading the country’s legal team. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of the role of an Attorney General, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of this significant position.
What is an Attorney General?
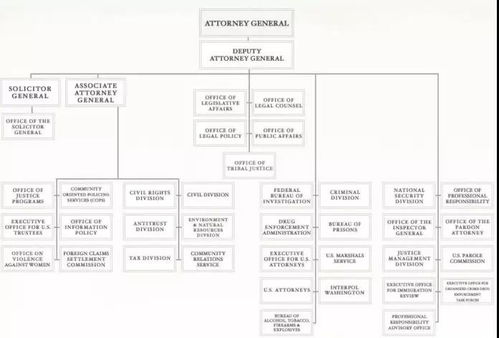
An Attorney General is the highest-ranking government official responsible for legal matters. The position varies in its scope and responsibilities depending on the country, but generally, the Attorney General is responsible for providing legal advice to the government, representing the government in legal proceedings, and ensuring that the government’s actions are legally sound.
Responsibilities of an Attorney General

Here are some of the key responsibilities of an Attorney General:
-
Legal Advice: One of the primary responsibilities of an Attorney General is to provide legal advice to the government on various issues, including legislation, executive decisions, and policy matters.
-
Representation: The Attorney General represents the government in legal proceedings, including court cases, appeals, and other legal disputes.
-
Enforcement of Laws: The Attorney General is responsible for ensuring that laws are enforced and that justice is served. This includes overseeing the work of government lawyers and law enforcement agencies.
-
Public Interest Litigation: The Attorney General can initiate legal action in the public interest, such as challenging unconstitutional laws or protecting the rights of individuals or groups.
-
International Legal Matters: The Attorney General may also be involved in international legal matters, such as negotiating treaties and agreements, and representing the country in international legal disputes.
Qualifications and Appointment

The qualifications for becoming an Attorney General vary by country, but generally, the following criteria are common:
-
Legal Background: Most Attorneys General have a background in law, often holding a law degree and having several years of legal experience.
-
Professional Reputation: A strong professional reputation and a record of successful legal work are often required.
-
Political Affiliation: In some countries, the Attorney General is appointed by the head of state or government, and political affiliation may be a factor in the appointment.
Here is a table showing the qualifications and appointment process for some countries:
| Country | Qualifications | Appointment Process |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Law degree, several years of legal experience | Appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate |
| United Kingdom | Qualification as a barrister or solicitor | Appointed by the Queen on the recommendation of the Prime Minister |
| India | Law degree, several years of legal experience | Appointed by the President on the recommendation of the Prime Minister |
Challenges and Controversies
Despite the important role of an Attorney General, the position is not without its challenges and controversies. Some of the common challenges include:
-
Political Pressure: Attorneys General may face political pressure to take certain actions or make specific decisions, which can compromise their independence.
-
Conflict of Interest: In some cases, the Attorney General may have a conflict of interest, such as representing the government in a legal dispute involving a family member.
-
Public Scrutiny: The Attorney General is often under intense public scrutiny, and any perceived failure to fulfill their duties can lead to criticism and controversy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the role of an Attorney General is a critical one, serving as the government’s chief legal advisor and ensuring that the government’s actions are legally sound. While the position varies in its scope and responsibilities depending on the country, the key responsibilities remain the same: providing legal advice, representing the government in legal proceedings, and ensuring that laws










