How Does AR Technology Work?
Augmented Reality (AR) has become an integral part of our daily lives, from gaming to education and even in the medical field. But how exactly does this technology work? Let’s delve into the intricacies of AR and understand its functioning from multiple dimensions.
Understanding the Basics

Augmented Reality is a technology that overlays digital information onto the real world. This is achieved by using a device, such as a smartphone, tablet, or AR glasses, to capture the real-world environment and then superimpose digital elements onto it. These digital elements can be anything from text, images, 3D models, or even interactive objects.
The Technology Behind AR
AR technology relies on several key components to function effectively:
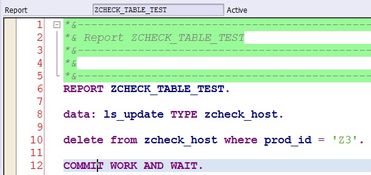
-
Camera: The camera captures the real-world environment and sends the data to the AR software.
-
Processor: The processor analyzes the camera data and determines the position and orientation of the device in the real world.
-
Display: The display shows the augmented content over the real-world environment.
-
Software: The software processes the camera data, determines the position and orientation of the device, and generates the augmented content.
Types of AR
There are several types of AR, each with its own unique characteristics:
-
Marker-based AR: This type of AR uses physical markers, such as QR codes or AR tags, to trigger the augmented content. The markers are recognized by the camera, and the corresponding content is displayed.
-
Markerless AR: Unlike marker-based AR, markerless AR does not require any physical markers. Instead, it uses computer vision algorithms to recognize and track the real-world environment.
-
Location-based AR: This type of AR uses GPS or other location-based services to determine the user’s position and display relevant augmented content.
How AR is Created
Creating AR content involves several steps:
-
Designing the content: The first step is to design the augmented content, which can be text, images, 3D models, or interactive objects.
-
Creating the assets: The next step is to create the assets required for the AR content, such as 3D models, textures, and animations.
-
Developing the software: The AR content is then integrated into the AR software, which processes the camera data and displays the augmented content.
-
Testing and refining: Finally, the AR content is tested on various devices to ensure it works correctly and is user-friendly.
Applications of AR
AR technology has a wide range of applications across various industries:
-
Education: AR can be used to create interactive learning experiences, allowing students to visualize complex concepts in a more engaging way.
-
Healthcare: AR can assist surgeons during operations, provide real-time information to patients, and help in training medical professionals.
-
Retail: AR can be used to provide virtual try-ons for clothing and accessories, allowing customers to see how they would look before making a purchase.
-
Entertainment: AR games and apps have become increasingly popular, offering immersive experiences that blend the real world with digital content.
Challenges and Future of AR
While AR technology has made significant advancements, there are still challenges to be addressed:
-
Hardware limitations: Current AR devices, such as smartphones and AR glasses, have limited processing power and battery life.
-
Privacy concerns: AR technology often requires access to the user’s camera and location data, raising privacy concerns.
-
Content creation: Creating high-quality AR content can be time-consuming and expensive.
However, the future of AR looks promising. As hardware becomes more advanced and software becomes more accessible, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of AR in our daily lives.
Table: Comparison of Different Types of AR
|
|
|---|







