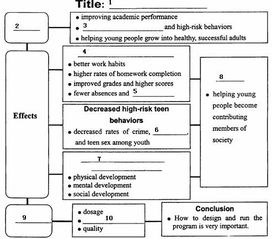
Difference Between RNP Approach and RNP AR Approach
When it comes to modern aviation navigation, the terms RNP and RNP AR are often used interchangeably, but they represent distinct concepts with significant differences. In this article, we will delve into the nuances of these two approaches, exploring their definitions, applications, and the technology behind them.
What is RNP Approach?
The Required Navigation Performance (RNP) approach is a type of instrument approach procedure that allows aircraft to fly precise paths with minimal reliance on ground-based navigation aids. RNP is designed to enhance safety, reduce fuel consumption, and improve operational efficiency.
RNP is characterized by its ability to define a navigation corridor with a specific width, known as the navigation corridor width (NCW). The NCW is determined by the aircraft’s navigation performance requirements (RNP min) and the required navigation performance (RNP) value. The RNP min is the minimum navigation performance that the aircraft must meet to fly the approach, while the RNP value is the total navigation performance required for the entire flight.
What is RNP AR Approach?

The RNP AR (Area) approach is a subset of the RNP approach that is specifically designed for terminal operations. RNP AR is used to provide precise navigation for aircraft during the final approach phase, ensuring they land safely and accurately within the designated runway environment.
One of the key differences between RNP and RNP AR is that RNP AR approaches are typically used in areas with limited ground-based navigation aids, such as remote airports or areas with complex terrain. RNP AR approaches can be flown using a combination of satellite-based navigation systems, such as GPS, and ground-based navigation aids, such as VORs and ILSs.
Technology Behind RNP and RNP AR Approaches
The technology behind RNP and RNP AR approaches is based on the Global Positioning System (GPS) and other satellite-based navigation systems. These systems provide aircraft with accurate position, velocity, and time information, allowing them to navigate with high precision.
GPS receivers on board the aircraft receive signals from multiple satellites to determine their position. The accuracy of the GPS position is then enhanced using differential GPS (DGPS) techniques, which correct for errors in the satellite signals. This enhanced accuracy is crucial for RNP and RNP AR approaches, as it allows aircraft to fly within the narrow navigation corridors defined by these approaches.
Applications of RNP and RNP AR Approaches
RNP and RNP AR approaches have been widely adopted by airlines and airports around the world. Some of the key applications of these approaches include:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduced Fuel Consumption | RNP and RNP AR approaches allow aircraft to fly more direct routes, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. |
| Improved Safety | The precision of RNP and RNP AR approaches enhances safety by reducing the risk of controlled flight into terrain (CFIT) and runway incursion. |
| Increased Operational Efficiency | RNP and RNP AR approaches enable airlines to operate more efficiently by reducing flight times and increasing the number of flights per day. |
| Enhanced Airspace Capacity | RNP and RNP AR approaches allow for more efficient use of airspace, leading to increased capacity at airports. |
In conclusion, the RNP and RNP AR approaches are advanced navigation techniques that have revolutionized aviation. By providing precise navigation and improved safety, these approaches have become an essential part of modern aviation operations.








