Understanding AR and MR: A Comprehensive Guide
Augmented Reality (AR) and Mixed Reality (MR) have become increasingly popular in recent years, transforming various industries from entertainment to healthcare. If you’re new to these technologies, you might be wondering what they are and how they differ. In this article, we’ll delve into the meanings of AR and MR, their applications, and the key differences between them.
What is Augmented Reality (AR)?
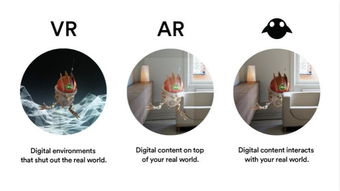
Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that overlays digital information onto the real world. It enhances the user’s perception of reality by adding virtual elements to the physical environment. These elements can be anything from text, images, and videos to 3D models and animations.
AR is often used in mobile applications, where the camera of a smartphone or tablet captures the real-world environment and overlays digital content on top of it. Some popular examples of AR applications include:
- Navigation Apps: AR navigation apps like Google Maps provide real-time directions and information by overlaying digital maps onto the user’s view of the world.
- Shopping Apps: AR shopping apps allow users to visualize products in their own space before making a purchase.
- Education and Training: AR is used in educational apps to provide interactive learning experiences and simulate real-world scenarios.
What is Mixed Reality (MR)?

Mixed Reality (MR) is a broader term that encompasses both Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR). While AR overlays digital content onto the real world, MR combines real and virtual elements to create a seamless experience. In MR, the virtual and physical worlds coexist, allowing users to interact with both simultaneously.
MR can be experienced through various devices, including smartphones, tablets, and specialized headsets. Some key features of MR include:
- Full Immersion: MR provides a more immersive experience compared to AR, as it allows users to interact with both the real and virtual worlds.
- Real-Time Interaction: Users can interact with virtual objects as if they were real, enabling more engaging and interactive experiences.
- Collaboration: MR facilitates collaboration between users in different locations, as they can share the same virtual space.
Applications of AR and MR
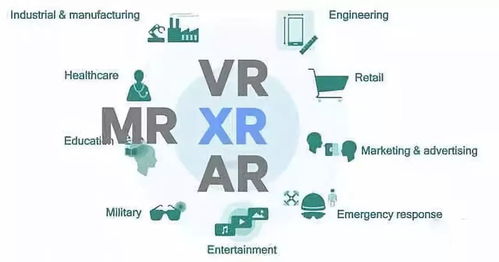
AR and MR have a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some examples:
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | Medical training, patient care, and remote surgery |
| Education | Interactive learning experiences, virtual field trips, and language learning |
| Entertainment | Video games, virtual concerts, and interactive storytelling |
| Manufacturing | Design and prototyping, assembly line training, and quality control |
| Real Estate | Virtual property tours, interior design, and space planning |
These applications highlight the versatility of AR and MR technologies, as they can be adapted to various fields and industries.
Differences Between AR and MR
While AR and MR are closely related, there are some key differences between the two technologies:
- Scope: AR primarily overlays digital content onto the real world, while MR combines real and virtual elements to create a more immersive experience.
- Immersiveness: AR is generally less immersive than MR, as it only overlays digital content onto the real world. MR, on the other hand, allows users to interact with both the real and virtual worlds simultaneously.
- Applications: AR is more commonly used in mobile applications, while MR is often used in specialized headsets and devices that provide a more immersive experience.
In conclusion, understanding the meanings of AR and MR, as well as their applications and differences, can help you appreciate the potential of these technologies in various industries. As these technologies continue to evolve, we can expect to see even more








