What is AP AR in Accounting?
Accounting is a complex field that involves various processes and concepts. Two of the most crucial aspects of accounting are Accounts Payable (AP) and Accounts Receivable (AR). Understanding these two components is essential for any business to manage its finances effectively. In this article, we will delve into the details of AP and AR, explaining their significance, processes, and best practices.
Accounts Payable (AP)
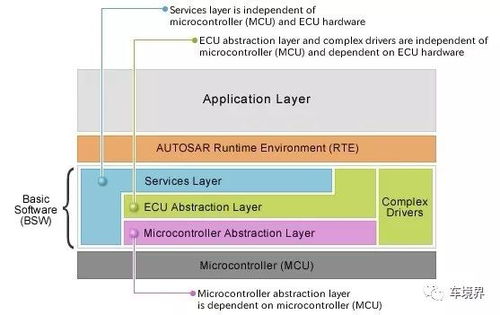
Accounts Payable refers to the money that a company owes to its suppliers, vendors, and creditors. It is a liability on the company’s balance sheet and represents the company’s obligations to pay for goods and services received but not yet paid for. Here’s a closer look at the key aspects of AP:
-
Recording Transactions: When a company purchases goods or services on credit, it records the transaction in its accounting system. The purchase is debited to an expense account, and the corresponding credit is made to the Accounts Payable account.
-
Payment Process: The company then pays the supplier or vendor within the agreed-upon terms, which could be a net 30, net 60, or any other agreed-upon period.
-
Vendor Management: Effective vendor management is crucial in AP. This involves maintaining good relationships with suppliers, negotiating favorable terms, and ensuring timely payments.
-
AP Automation: Many companies use accounting software to streamline their AP processes. Automation can help reduce errors, save time, and improve efficiency.
Accounts Receivable (AR)

Accounts Receivable represents the money that a company is owed by its customers for goods or services sold on credit. It is an asset on the company’s balance sheet and reflects the company’s right to receive payment. Here are the key aspects of AR:
-
Recording Transactions: When a company sells goods or services on credit, it records the transaction in its accounting system. The sale is debited to the Accounts Receivable account, and the corresponding credit is made to the revenue account.
-
Invoice Management: Invoices are crucial in AR. They provide detailed information about the sale, including the amount due, payment terms, and due date. Proper invoice management ensures accurate and timely payments.
-
Collection Process: Collecting payments from customers is a critical aspect of AR. This involves following up on late payments, applying late fees, and maintaining good customer relationships.
-
AR Automation: Similar to AP, many companies use accounting software to automate their AR processes. Automation can help reduce errors, save time, and improve efficiency.
Comparing AP and AR
While AP and AR are distinct processes, they are interconnected and play a vital role in a company’s financial health. Here’s a comparison of the two:
| Accounts Payable (AP) | Accounts Receivable (AR) |
|---|---|
| Liability | Asset |
| Money owed to suppliers | Money owed by customers |
| Debited when purchasing goods/services on credit | Debited when selling goods/services on credit |
| Credited when paying suppliers | Credited when receiving payments from customers |
Best Practices for Managing AP and AR
Effective management of AP and AR is crucial for maintaining a healthy cash flow and financial stability. Here are some best practices to consider:
-
Implement an Efficient Payment Process: Establish clear payment terms and follow up on late payments promptly.
-
Use Accounting Software: Invest in accounting software to streamline your AP and AR processes.
-
Regularly Review Aging Reports: Aging reports help identify late payments and take appropriate actions.
-
Monitor Cash Flow








